World’s largest-to-be smartphone market
Recent figures show that developed countries now have or will have very soon, over 50% smart phone penetration rates, including the USA which is the third most populous nation with 311 million inhabitants.
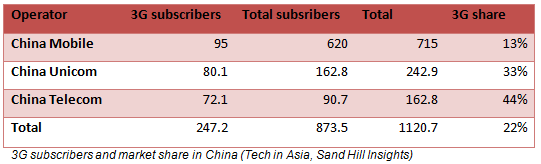
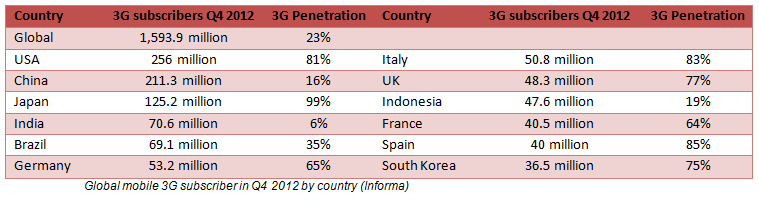
On the other hand, China is still a developing country with poor 3G penetration rates estimated at 22% of the 1.12Bn subscribers of as of January 2013. (Tech in Asia, Sand Hill Insights) This is poor if we compare it to the USA’s 81% and slightly less than the global average which stood at 23% at the end of 2012 (Informa). But demographics oblige the sheer number of subscribers in China and its near neighbour and rival India, will very soon transform these two countries into the world’s biggest smartphone markets.
The country’s mobile penetration rate is good (82.6%) and 49.1% of the 260 million phones sold in China in 2012 were smartphones which shows that the country is adapting rapidly to technology with the help of applications. Smartphones and applications go hand in hand, and a number of Chines apps have been particularly successful. WeiXin (or WeChat) is a good example of an application adopted by Chinese smartphone users. It is an instant messaging program  similar to WhatsApp, KakaoTalk, or Viber that offers many social features and has attracted over 240 million Chinese. (as well as 60 millionother people in the world).
similar to WhatsApp, KakaoTalk, or Viber that offers many social features and has attracted over 240 million Chinese. (as well as 60 millionother people in the world).
Such is its popularity of that even older users, most of whom were still technolo-illiterate not so long ago have converted to smartphones and quickly adopted the features they provide.
Of course these over the top services (OTT) reduce revenues from the more traditional SMS and MMS which are provided by the statet owned telecommunication companies (China Mobile, China Unicom, China Telecom)So it is not surprising that these companies have teamed up against applications that offer free mobile services such as WeiXin/WeChat in order to reduce competition. They are trying to charge such applications that are currently free to use with the help of goverment departments, an idea not welcomed by the users.
Leader in production & exportation
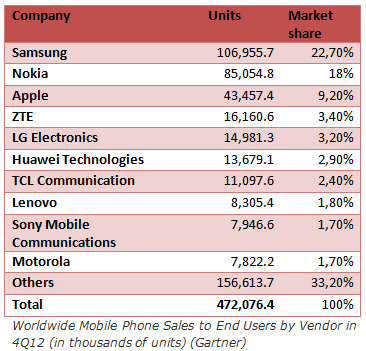
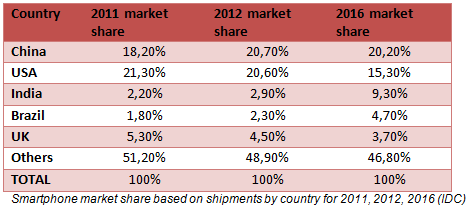
Samsung (Republic of Korea), Nokia (Finland) and Apple (United States of America) are the top three mobile phone manufacturers and together their sales account for nearly 50% of all phones shipped. However of the the 1.6 billion units produced in 2012, 1.015 billion, or 63.4%, came out of China (MarketResearchReports). More significantly the country has become the number one smartphone producer with 224 million shipments made in 2012, overtaking the USA. This figure is expected to reach 301 million this year and even 457 million by 2017 (IDC).
In the last quarter of 2012 in China, Samsung still was the dominant brand with 18.5% of the smartphone market share, followed by Huawei (12%), Lenovo (11.7%), Coolpad (10.4%) and ZTE (9.5%) according to Strategy Analytics. Apple only took the sixth place with 8.5% (Canalys).
Despite that encouraging position, the USA still made more profit on its sales than China, which focuses more on budget smartphones like the Xiaomi M1 (1299 RMB – approx. €160) or the Oppo X903 (2,999 RMB – approx. €370) Budget does not necessarily mean the phones can not compete against higher-end products. The Xiaomi M2 for example (1,999 RMB – approx. €250) manage to sell 50,000 phones in under 3 minutes, when it was launched in October last year.
Here are the characteristics.
- 1.5 GHz quad-core Qualcomm Snapdragon S4 Pro APQ8064 processor
- 4.0 inch multi-touch capacitive touchscreen
- Sharp ASV TFT screen, 720P
- 2GB DDR3 RAM
- 12MP CMOS camera, auto-focus, LED flashlight, 1.3MP front camera
- Li-ion battery, 2000mAh
Could we see similar Chinese phones being launched in Europe? Yes! Already Oppo, best known in Europe for it’s Blu-ray players has introduced direct online sales of its Oppo Find 5 smartphone. We can expect more Chinese manufacturers to adopt this tactic if Oppo are successful.
Huge investments in 4G deployment
In terms of infrastructure the Chinese authorities have hastened the development of the country’s network and plan to issue 4G permits in advance. China Mobile, the biggest and state-owned mobile operator in China, is ready to spend over 190.2 billion RMB (approx. 23.5 billion euros) on its network, of which 21.9% will be used to build its 4G network.
Although Ericsson is the biggest player the telecommunications equipment market, the company only succeeded in winning 8.1% of China Telecom’s tender for Time Division-Long Term Evolution (TD-LTE) in 2012, quite a way behind Alcatel Lucent with its 14.5% market share.
In comparison, the government-helped Chinese companies Huawei, ZTE and Datang Mobile shared most of the market, with the first two companies having respectively 23.8% and 22.1% of the total contracts, the rest being split between Nokia Siemens Networks and New Postcom.
The main reasons for privileging local firms is because China developed its own 3G network which is based on TD-SCDMA technology and has the choice to either upgrade its existing network through the same local companies, or to build a new and more efficient one allowing more competition. For now, the government chose to reduce its costs by choosing the local option but it is still thinking about which model to adopt.
According to TheNextWeb, China Mobile has already deployed over 200,000 TD-LTE stations across 150 places in China, suggesting that the operator will be ready to launch its 4G network in August.
In conclusion, the Chinese mobile market and smartphone industry both look promising; with an increasing penetration rate indicative of the country’s modernization. Moreover, even if the manufacturers were and are still producing for foreign brands such as Apple or Samsung, Chinese companies such as Xiaomi, Meizu, Coolpad and a few others are starting to surface in the smartphone world with phones that begin to compete on both price and quality. The rise of these firms and the government’s wish to quickly expand a 4G network in the country are the key elements in the success of not only the smartphone industry in China, but also in other countries as well. Huawei and ZTE will strengthen their position in the world and Chinese mobile brands will challenge the current market leaders.
For more information see:
- http://www.gartner.com/newsroom/id/2335616
- http://www.itnewsafrica.com/2013/01/global-mobile-phone-shipments-rose-to-1-6-billion-in-2012/
- http://www.globaltimes.cn/content/738925.shtml
- http://www.allvoices.com/contributed-news/14613140-global-and-china-mobile-phone-cell-phone-assembly-market-to-2012-2013-available-at-marketresearchreportsbiz
- http://www.engadget.com/2012/03/16/china-may-surpass-us-in-smartphone-shipments/
- http://www.forbes.com/sites/chuckjones/2013/02/24/china-carriers-smartphone-3g-penetration-only-at-22/
- http://phys.org/news/2013-03-smartphone-sales-million.html
- http://mobithinking.com/mobile-marketing-tools/latest-mobile-stats/
- http://www.zdnet.com/china-4g-licenses-to-be-issued-in-2013-7000004009/
- http://technode.com/2013/02/08/49-percent-of-mobile-phones-sold-in-china-in-2012-were-smartphones/
- http://www.fool.com/investing/international/2013/04/03/innovation-or-stagnation-in-the-chinese-mobile-mar.aspx
- http://www.china.org.cn/business/2013-05/08/content_28760867.htm
- http://micgadget.com/17858/10-chinese-budget-smartphones-that-could-kill-the-iphone/
- http://thenextweb.com/asia/2013/04/29/china-mobile-reportedly-targeting-august-2013-launch-for-chinas-first-4g-network/